Understanding the HHS Criteria
HomVEE relies on a set of criteria specified by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services for evidence of effectiveness, the “HHS criteria”. These criteria require that favorable findings for a home-visiting model be replicated in one or more of HomVEE’s eight outcome domains. A home-visiting model must meet these criteria to earn a HomVEE evidence-based designation.
HomVEE recognizes that other systematic reviews may use different criteria to evaluate evidence of effectiveness. Thus, an evidence-based model in the context of HomVEE might or might not meet requirements for evidence of effectiveness according to other systematic reviews.
HHS criteria for evidence-based models
To meet HHS’ criteria for an “evidence-based early childhood home visiting service delivery model,” models must meet at least one of the following criteria:
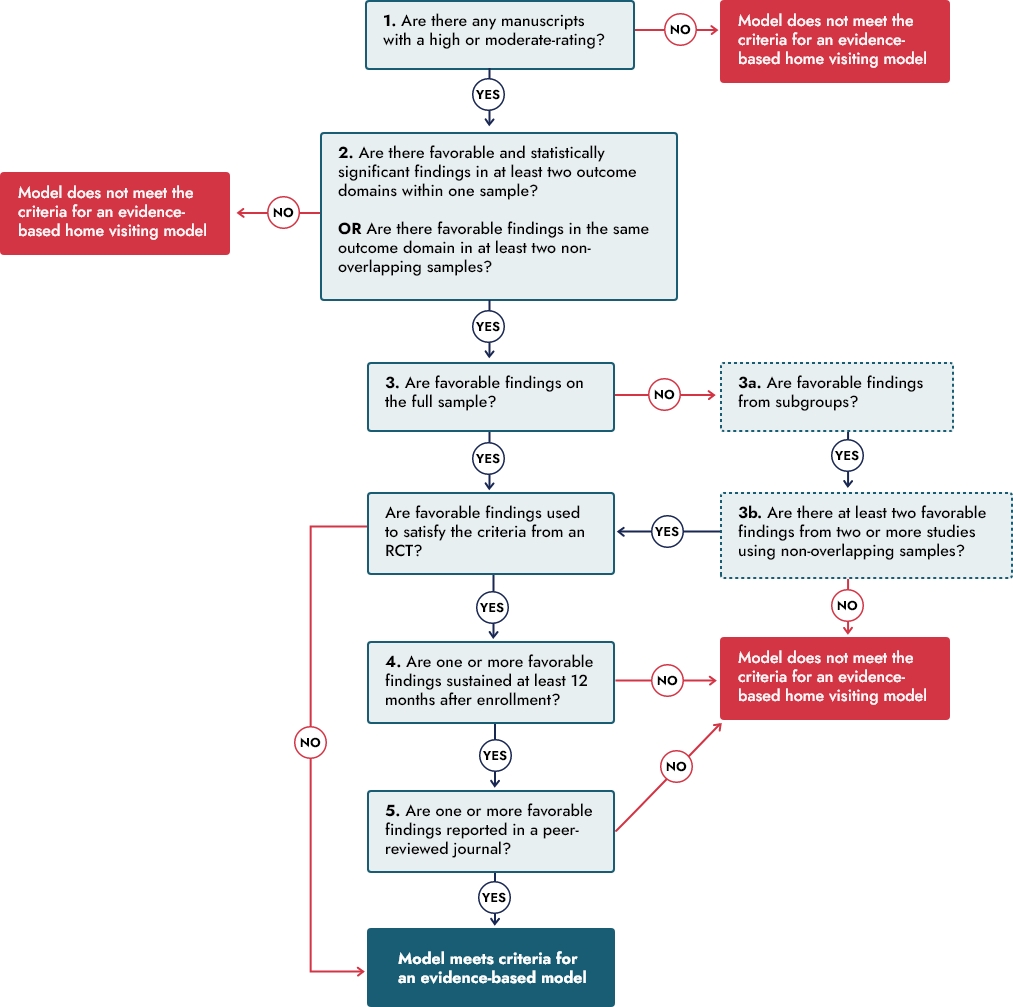
- At least one high- or moderate-rated impact study of the model finds favorable (statistically significant) impacts in two or more of the eight outcome domains.
- At least two high- or moderate-rated impact studies of the model (using non-overlapping analytic study samples) find one or more favorable (statistically significant) impacts in the same domain.
In both cases, the impacts must either (1) be found in the full sample or (2) if found for subgroups but not for the full sample, be replicated in the same domain in two or more studies using non-overlapping analytic study samples. Additionally, following the statute, if the model meets the above criteria based on findings from randomized controlled trial(s) only, then two additional requirements apply. First, one or more favorable (statistically significant) impacts must be sustained for at least one year after program enrollment. Second, one or more favorable (statistically significant) impacts must be reported in a peer-reviewed journal.
These criteria are consistent with the MIECHV statutory requirements: 42 U.S.C. 711(d)(3)(A)(i)(I)
HomVEE assesses whether or not a model meets the criteria for an evidence-based model by considering the following:
- Is there well-designed research?
All findings used to meet the criteria must receive high or moderate ratings. - Is the impact replicated?
Favorable findings must be in at least two different outcome domains, or in the same domain in at least two non-overlapping study samples. - Are favorable impacts found on the full sample?
If found for subgroups of the full sample instead, the favorable findings must be replicated in the same outcome domain in at least two nonoverlapping study samples.
IF favorable findings to satisfy the criteria are from an RCT, two additional criteria must be met:
- Is the impact sustained?
At least one favorable finding must be measured at least 12 months after participant enrollment. - Is the research peer-reviewed?
At least one favorable finding must be reported in a peer-reviewed journal.
Full text description of Figure 1
For more information, see the HomVEE Handbook of Procedures and Evidence Standards.